A computer may look simple from the outside, but a lot is happening beneath that casing.
Every task, from opening a browser to saving a file, depends on several key components working together in the background.
Understanding these parts makes it easier to know why a system runs fast, slows down, or struggles with specific tasks.
This guide explains what a computer is clearly and practically, focusing on what each component does and why it matters.
No matter if you’re looking to speed up your PC, replace a part, or just curious about how it all works, this is for you!
Don’t worry, no complex tech terms here, just simple explanations to get you up to speed in no time.
How Do Computer Components Work Together?
When you press the power button on a computer, the power supply delivers electricity to the motherboard, which activates the CPU and begins the startup sequence.
The CPU then retrieves instructions from the storage drive and uses RAM to temporarily store data needed to load the operating system and essential services.
The motherboard serves as the central hub, allowing all components to communicate and share data efficiently.
During startup, the system checks that key hardware components are present and functioning before continuing.
Once running, overall performance depends on how well these parts work together.
Slow storage, limited RAM, or an underpowered processor can create bottlenecks that reduce system responsiveness and affect everyday tasks.
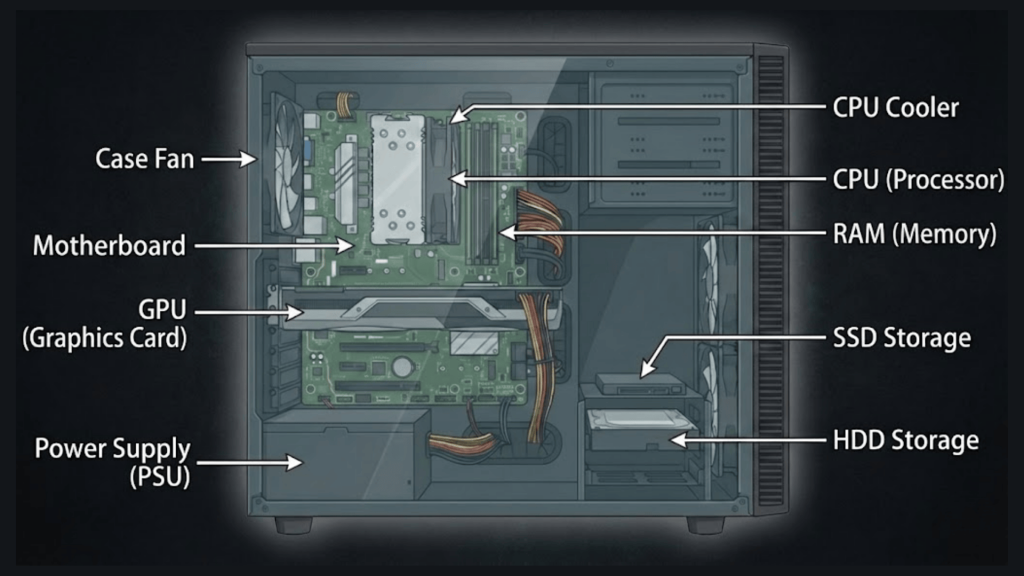
Key Components of Inside Your Computer
Understanding the key parts inside your computer helps you make informed decisions about upgrades and performance. Here’s a simple breakdown of each crucial component.
1. The Motherboard
The motherboard is the main circuit board in your computer, connecting all the essential parts.
It’s called the “motherboard” because it houses everything and connects the CPU, RAM, storage, and more.
Think of it like a city’s road system, linking all neighborhoods (components).
It’s crucial when buying or upgrading, as it determines what parts are compatible and how well your computer performs.
2. The CPU (Processor)
The CPU processes instructions and calculations, making it the brain of your computer.
It handles everything from running apps to executing commands.
CPUs have cores, which help with multitasking, and clock speed, which affects how quickly tasks are processed.
Intel and AMD are the two leading brands, with Intel focusing on high speed and AMD offering good value for multi-core performance.
It directly impacts how quickly your computer responds when you open a file.
3. RAM
RAM is the short-term memory of your computer. It holds data that’s actively in use, like apps you’re working on.
Unlike storage, which retains everything permanently, RAM is cleared when you shut down your PC.
More RAM means your computer can handle more tasks at once, making multitasking easier.
If you use many apps at once, 16GB or 32GB of RAM can make a big difference, much like having a bigger desk to work on.
4. Storage Drives
Storage is where your files, programs, and operating system live.
Hard Drives (HDDs) are cheaper but slower, while Solid State Drives (SSDs) are faster and more durable.
SSDs load apps and files more quickly, making your computer feel faster.
Storage capacity depends on your needs: 500GB for basic use, or 1TB or more for gaming and heavy media use.
Newer NVMe drives are even faster than SSDs, further improving load times.
5. Graphics Card (GPU)
The GPU handles all the visual aspects of your computer. It processes everything you see on your screen, from videos to games.
Integrated graphics are built into the CPU, while dedicated graphics cards offer more power for tasks such as gaming, video editing, and design.
If you’re into gaming or creative work, a dedicated GPU is essential.
It works closely with your monitor to render graphics in high quality.
6. Power Supply Unit
The PSU converts power from your wall outlet into usable electricity for your computer.
The wattage determines how much power your computer needs, and a higher-quality PSU ensures stable performance.
It powers the motherboard, CPU, and other components.
Choosing a reliable PSU can prevent crashes or hardware damage, so don’t skimp on quality when upgrading.
7. Cooling System
Computers need cooling to prevent overheating, which can damage components and slow down performance.
There are two main types of cooling: fans, which are simple and common, and liquid cooling, which is more efficient for high-performance setups.
Thermal paste helps improve heat transfer between the CPU and cooler.
Signs your cooling system might not be working include strange noises, slow performance, or unexpected shutdowns.
Proper cooling ensures your system runs smoothly and lasts longer.
HDD vs SSD: Key Differences Explained
When deciding between an HDD and an SSD, it’s essential to understand the differences in speed, durability, capacity, and cost. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSD (Solid State Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower read/write speeds | Much faster read/write speeds |
| Durability | Prone to damage from movement | More durable, no moving parts |
| Capacity | Higher capacity for lower cost | Lower capacity, higher cost |
| Noise | It can be noisy due to moving parts | Quiet operation |
| Energy Efficiency | Consumes more power | Uses less power |
| Price | More affordable per GB | More expensive per GB |
How Does Your Computer Manage Memory?
Your computer uses a smart system to manage memory and keep things running smoothly, even when RAM fills up.
When you open programs, the operating system loads the most frequently used data into RAM for quick access.
If RAM gets full, the computer creates virtual memory by temporarily moving less-used data to your storage drive.
This process, called paging or swapping, allows your system to handle more tasks than RAM alone could support.
However, virtual memory is much slower than RAM since storage drives can’t match RAM’s speed.
This is why you notice slowdowns when too many programs are open: your computer is constantly swapping data between RAM and storage.
Common Signs Your Components Are Struggling
Understanding how your computer behaves under stress helps you identify which component is handling the workload. Here are common signs that specific parts are being pushed to their limits:
- CPU at full capacity: The computer becomes slow and unresponsive, fans spin louder, and programs take longer to open
- RAM running low: Frequent freezing, programs crash unexpectedly, switching between apps feels sluggish
- Storage drive struggling: Long boot times, delayed file saves, programs hang when loading large files
- GPU overloaded: Screen stuttering during games, video playback lags, graphics appear choppy or delayed
- Cooling system insufficient: Unexpected shutdowns, unusually hot case, loud fan noise, performance throttling
- Power supply issues: Random restarts, components not powering on, clicking sounds from the Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Conclusion
Now you understand how the main components inside a computer work together to handle every task you perform.
The CPU processes instructions, RAM provides quick access to active data, storage holds your files, and the GPU renders what you see on screen, all coordinated through the motherboard.
When you notice your system slowing down or behaving unusually, you can now identify which component might be the cause.
Whether it’s RAM running low during multitasking or your storage drive struggling to keep up, understanding these parts helps you make sense of your computer’s behavior.
The more you learn about how these components function, the better you’ll understand what’s happening inside that case every time you press the power button.
Which component surprised you the most? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Upgrade Individual Components?
Yes, components like RAM, storage, and GPUs can be upgraded for better performance, as long as they’re compatible with your motherboard.
How Long Do Components Typically Last?
Most components last 3 to 5 years, depending on usage. High-end parts like CPUs and GPUs can last longer.
What Component Makes the Most Significant Difference in Everyday Use?
The SSD improves everyday performance by speeding up boot times, app loading, and file access.