Wondering how to keep your home or business secure? An intrusion alarm system is one way to do that.
It’s designed to detect unauthorized entry and alert you if there’s a potential security breach. These systems are reliable, easy to set up, and offer peace of mind by keeping your property safe from theft or damage.
Whether you need basic protection or something more advanced, there are different types available to fit your needs.
From motion sensors to glass break detectors, an intrusion alarm can be customized to cover all areas of your property.
In this blog, I’ll explain how these systems work, the benefits they offer, and what to consider when choosing one.
Let’s take a closer look at how you can enhance your security.
What is an Intrusion Alarm System?
An intrusion alarm system is a security solution designed to detect unauthorized entry into a property.
It typically includes sensors, control panels, and alarms that work together to monitor different areas of a building.
The system uses motion detectors, door/window contacts, and sometimes glass break sensors to identify potential intrusions.
When any of these sensors are triggered, the system sends an alert, which can activate a loud alarm or notify the property owner and security services.
Modern intrusion alarms can be integrated with smart technology, allowing users to monitor and control them remotely through mobile apps.
This makes it easier to receive real-time updates and take action in case of a break-in.
Why are Intrusion Alarms Important?
Intrusion alarms play a crucial role in safeguarding property and ensuring safety.
They act as a first line of defense by detecting unauthorized entry, providing immediate alerts to property owners, or monitoring services.
These systems help deter potential burglars, as the presence of visible alarms or sensors signals that the property is being actively monitored.
Intrusion alarms can detect a range of threats, including motion, broken windows, and unauthorized door openings, ensuring timely responses to security breaches.
Many modern systems are equipped with smart technology, allowing remote monitoring and control, enhancing convenience and effectiveness.
By reducing response time and minimizing the risk of property damage or theft, intrusion alarms provide valuable protection.
How Does an Intrusion Alarm System Work?
An intrusion alarm system detects unauthorized entry into a home or building and alerts occupants or monitoring services.
The system uses sensors placed on doors, windows, and key areas to sense movement, opening, or vibration.
When a sensor is triggered, it sends a signal to a control panel. The panel verifies the event and activates alarms such as sirens, lights, or mobile alerts.
Many systems connect to a monitoring center that contacts the owner or emergency services if needed. Modern systems may include motion detectors, glass break sensors, and cameras for added coverage.
Some setups also link to smart devices, allowing remote arming and status checks.
By responding quickly to suspicious activity, these alarm system helps reduce theft, damage, and safety risks while offering consistent protection day and night for homes and businesses alike.
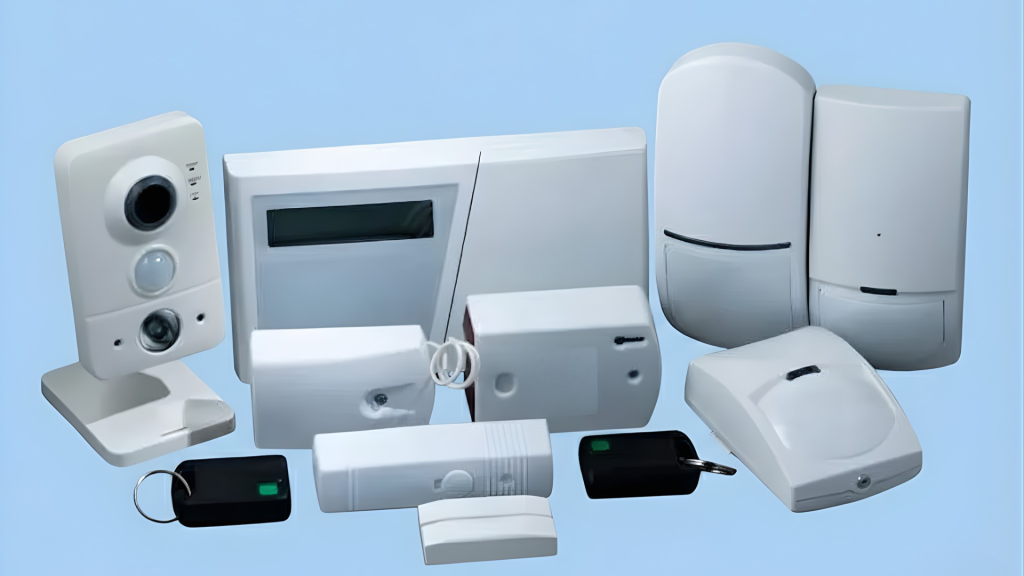
Key Components of an Intrusion Alarm System
An intrusion alarm system consists of several essential components that work together to provide comprehensive security for a property.
1. Control Panel
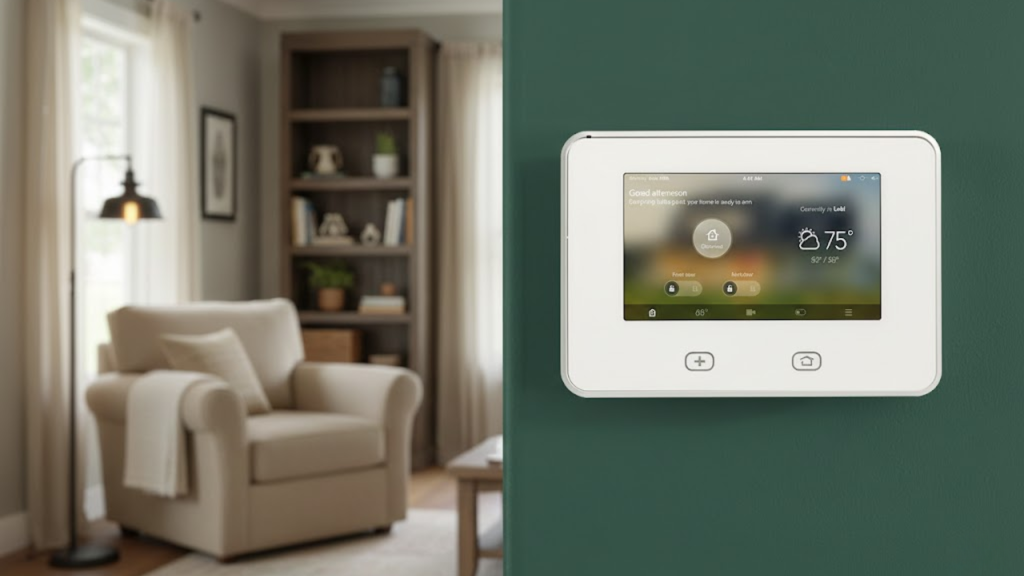
The control panel is the brain of an intrusion alarm. It connects all the components and processes the signals from various sensors.
Once it receives input from a sensor, it evaluates whether the system should trigger an alarm. The control panel can also send alerts to the monitoring center or the property owner.
Many modern control panels are equipped with touchscreen displays and can be integrated with mobile apps for remote control.
2. Sensors
Sensors are crucial for detecting movement or unauthorized entry within the property. They come in different types, such as motion detectors, door/window contacts, and glass break sensors.
Motion detectors sense movement within a defined area and are typically used in hallways, rooms, or large spaces.
Door/window contacts are triggered when a door or window is opened, while glass break sensors detect the sound of breaking glass.
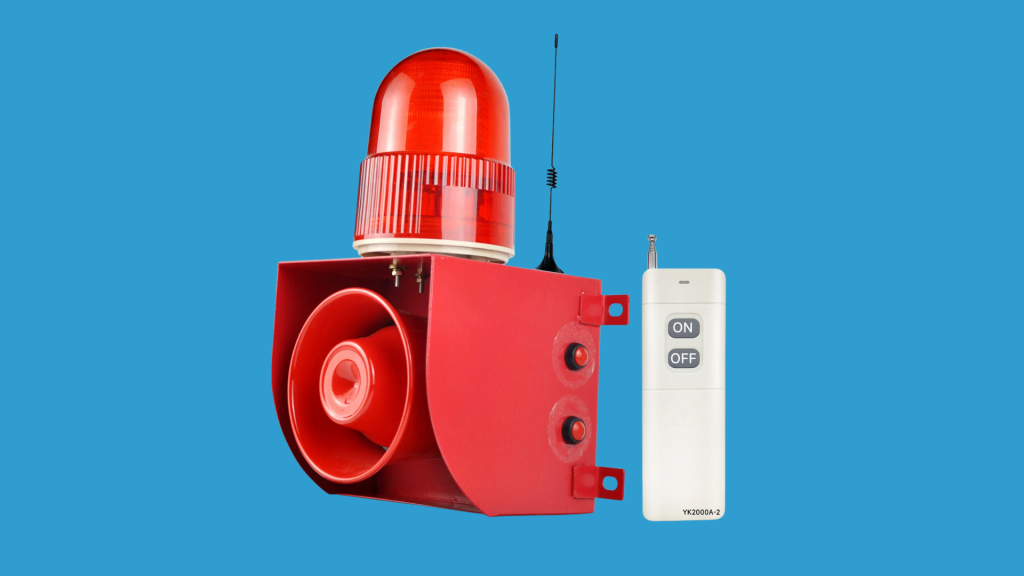
3. Siren or Alarm
The siren or alarm is a loud noise-generating device that sounds when an intrusion is detected.
It is a key component of the intrusion alarm system designed to alert both the property owner and anyone nearby about a potential threat.
Sirens can be installed inside or outside the building. An external siren is highly effective in alerting neighbors, while an internal siren can startle intruders and deter them from continuing their break-in.
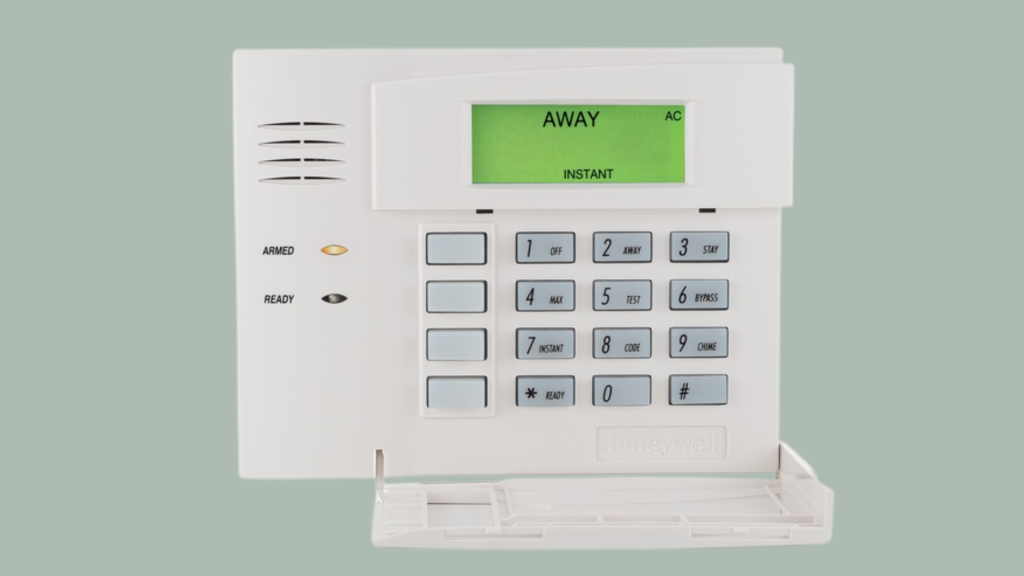
4. Keypad
The keypad is used to arm and disarm an intrusion alarm. It typically features buttons for entering security codes, arming or disarming the system, and accessing other settings.
Many keypads also display the status of the system, such as whether it is armed or in a specific mode like “stay” or “away.”
Some models may include additional features like panic buttons or the ability to control specific zones in the system.
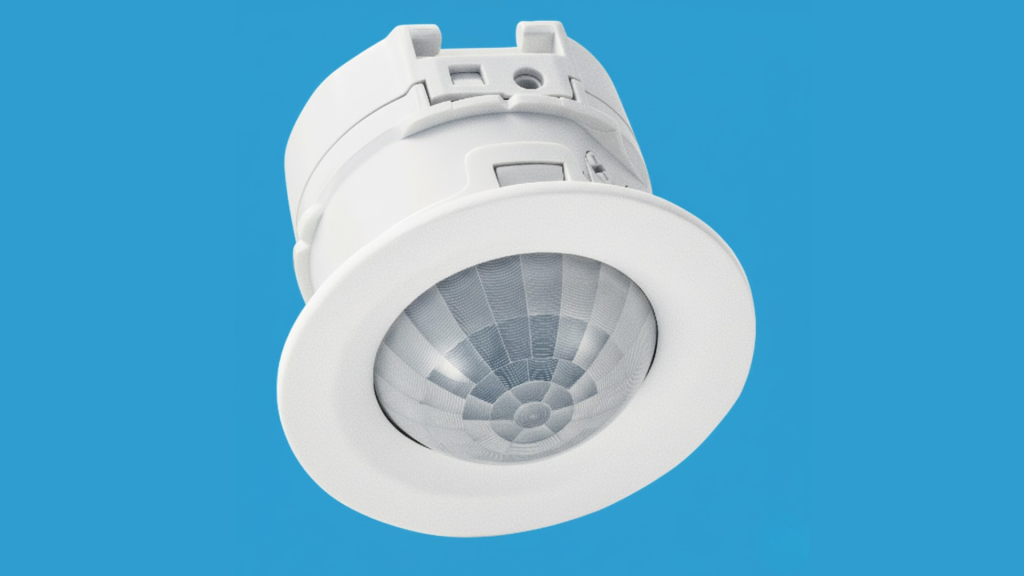
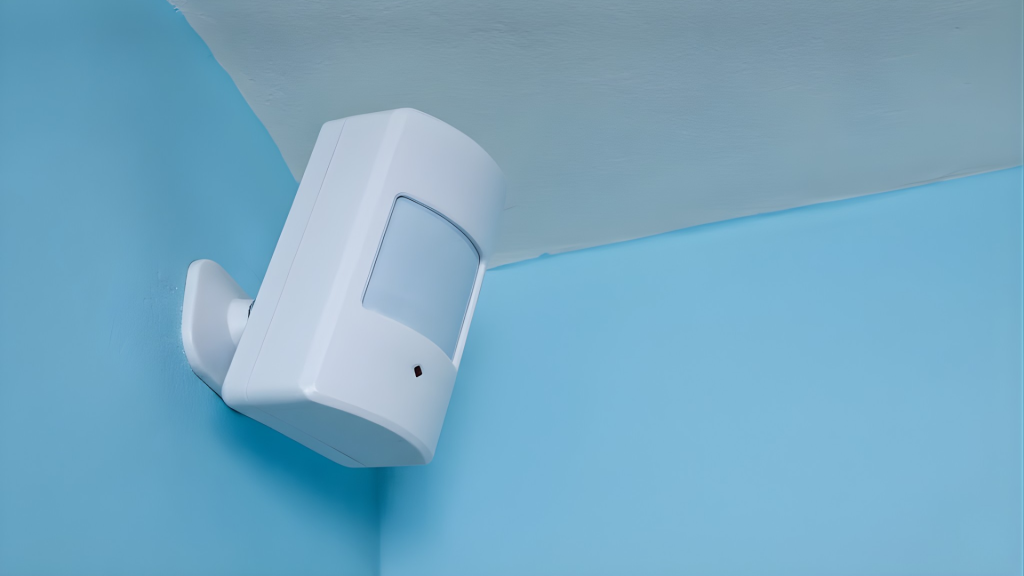
5. Motion Detectors
Motion detectors are specialized sensors designed to detect movement within a specific area.
They are an integral part of an intrusion alarm, often placed in hallways or large spaces to monitor for any unauthorized movement.
These detectors use infrared technology to sense changes in heat and motion, triggering an alert when movement is detected.
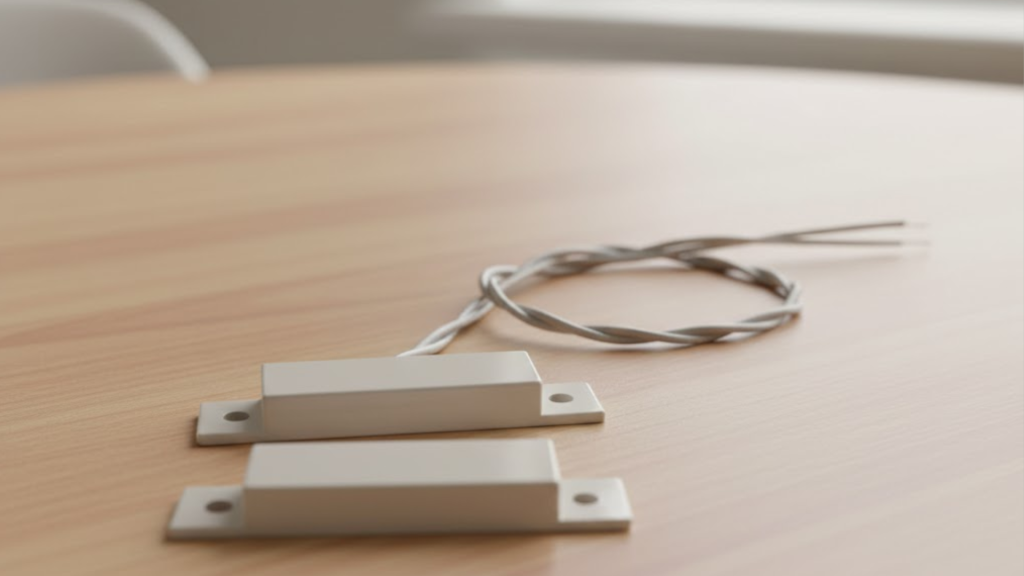
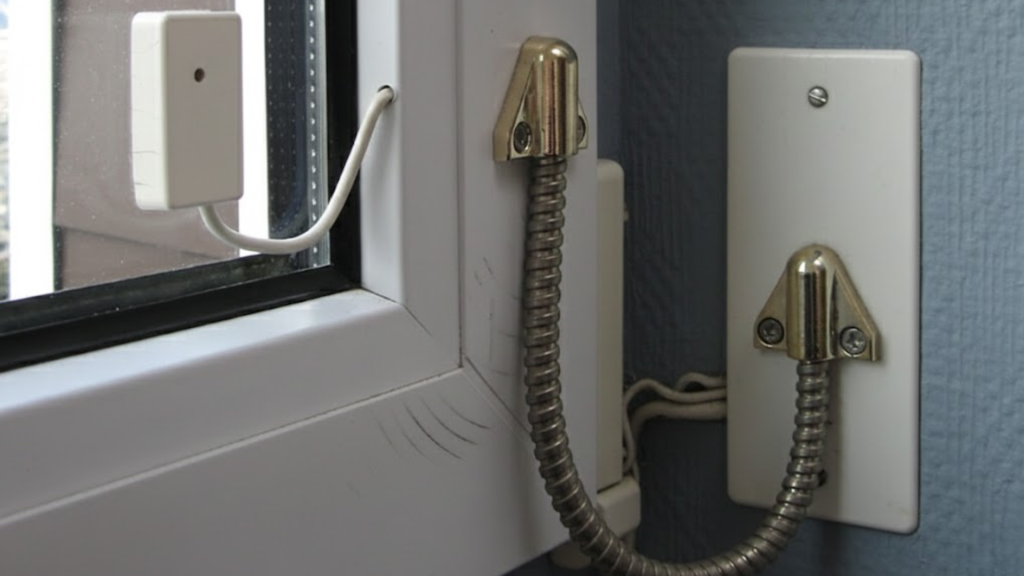
6. Door/Window Contacts
Door and window contacts are one of the most common components of an intrusion alarm. These devices consist of two parts: a magnet and a switch.
When the door or window is closed, the magnet and switch are aligned, and the system remains inactive. However, when a door or window is opened, the magnet moves away from the switch, triggering the alarm.
This component is particularly useful for monitoring entry points like doors and windows, helping to detect any unauthorized access to the building.
7. Glass Break Sensors
Glass break sensors are designed to detect the sound of breaking glass, an indicator of a potential break-in.
These sensors listen for specific frequencies created by glass breaking and send a signal to the control panel if they detect it.
By adding this component, an intrusion alarm system can provide additional protection by detecting break-ins even if the intruder bypasses other entry points like doors and windows.
Types of Intrusion Alarm Systems
There are various types of intrusion alarms, each offering different features and levels of protection to suit specific needs.
1. Wired Intrusion Alarm
A wired intrusion alarm is one of the most traditional and reliable types. It connects all components, such as sensors, keypads, and control panels, through physical wires.
This type offers consistent and stable performance, as there are no wireless signals that could be intercepted or disrupted.
However, installation can be more invasive, as it requires running wires throughout the property.
2. Wireless Intrusion Alarm
A wireless intrusion alarm system uses radio signals to connect the sensors, control panel, and other components, eliminating the need for wires.
This system is easier and faster to install compared to wired systems, making it ideal for existing buildings or rental properties.
Wireless systems also offer flexibility in terms of placement and expansion. However, they may be vulnerable to interference or hacking, though modern encryption technology helps mitigate this risk.
3. Monitored Intrusion Alarm
A monitored intrusion alarm is connected to a professional monitoring center, which continuously watches over the property.
If the alarm is triggered, the monitoring center is immediately notified and will respond by contacting the property owner or dispatching emergency services.
This system provides an extra layer of security since professionals are constantly monitoring the property.
4. Unmonitored Intrusion Alarm
An unmonitored intrusion alarm does not connect to a professional monitoring service.
Instead, when the system detects an intrusion, it triggers a loud alarm or sends a notification directly to the property owner via phone or email.
These systems are cost-effective as they do not require ongoing monitoring fees. However, since there is no professional monitoring, the response time depends on the homeowner’s ability to react quickly.
5. Smart Intrusion Alarm
A smart intrusion alarm system integrates with smart home technology, allowing users to control and monitor the system remotely via smartphones or tablets.
It often includes features like mobile notifications, remote disarming, and integration with other smart devices like cameras, thermostats, and lighting.
With a smart intrusion alarm, users can receive alerts instantly and manage their security system from anywhere in the world.
6. Pet-Friendly Intrusion Alarm
Pet-friendly intrusion alarms are designed to allow pets to move around freely within the monitored area without triggering false alarms.
It typically uses advanced motion sensors that can differentiate between pets and humans, ensuring that pets of a certain size or weight do not activate the alarm.
This feature is ideal for homes with pets, as it reduces the risk of frequent, unnecessary alerts caused by animals. Pet-friendly systems help balance the needs of security with pet owners’ convenience.
7. Hybrid Intrusion Alarm
A hybrid intrusion alarm system combines the best features of wired and wireless systems.
It allows users to incorporate both wired and wireless components into the same system, offering flexibility for different areas of the property.
Hybrid systems are ideal for properties that require a more customizable setup, such as large homes or commercial spaces.
Tips for Choosing the Right Intrusion Alarm
Practical guidance to help select an intrusion alarm system by focusing on features, reliability, and long-term security needs.
- Assess property size: Choose a system that covers all doors, windows, and open areas based on the home or building layout.
- Choose monitoring type: Decide between professional monitoring or self-monitoring depending on response needs, budget, and availability during emergencies.
- Check system compatibility: Ensure the alarm works with existing smart devices, cameras, or access control systems for easier management.
- Review power backup: Look for battery or cellular backup options so the system stays active during power outages or network issues.
- Plan for expansion: Select a system that allows adding sensors, cameras, or features later as security needs change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an intrusion alarm system is a vital tool for ensuring the security of your property.
If you’re looking to protect your home or business, these systems offer peace of mind by detecting potential threats before they become a bigger issue.
With various types available, it’s easy to find one that fits your needs and budget. From wired to wireless, monitored to unmonitored, each system has its benefits.
If you’re ready to take your property security to the next level, it’s time to consider installing such alarm systems.
Don’t wait for a break-in to happen and be proactive in protecting what matters most.
Want to know more about choosing the right system? Drop a comment below, and let’s discuss the best options for you!