Have you ever walked into a perfectly climate-controlled room that seemed to anticipate your comfort needs?
Smart HVAC systems are changing how we heat, cool, and manage air quality in buildings today.
These advanced climate control solutions use technology to automatically adjust temperatures, monitor air quality, and reduce energy waste.
Unlike traditional systems that rely on manual thermostats, these smart systems learn your preferences and adapt to changing conditions throughout the day.
This guide explains what these systems are, how they function, and what makes them valuable for homeowners and building managers.
You’ll learn about the core components, real-world benefits, and practical applications that make these systems increasingly popular in residential and commercial spaces.
What is a Smart HVAC System?
A smart HVAC system automatically controls heating, cooling, and ventilation using sensors and connected software.
These systems differ from traditional HVAC equipment by collecting real-time data about temperature, humidity, and occupancy patterns.
Built-in intelligence allows them to make automated adjustments without constant manual input, learning from habits and responding to environmental changes throughout the day.
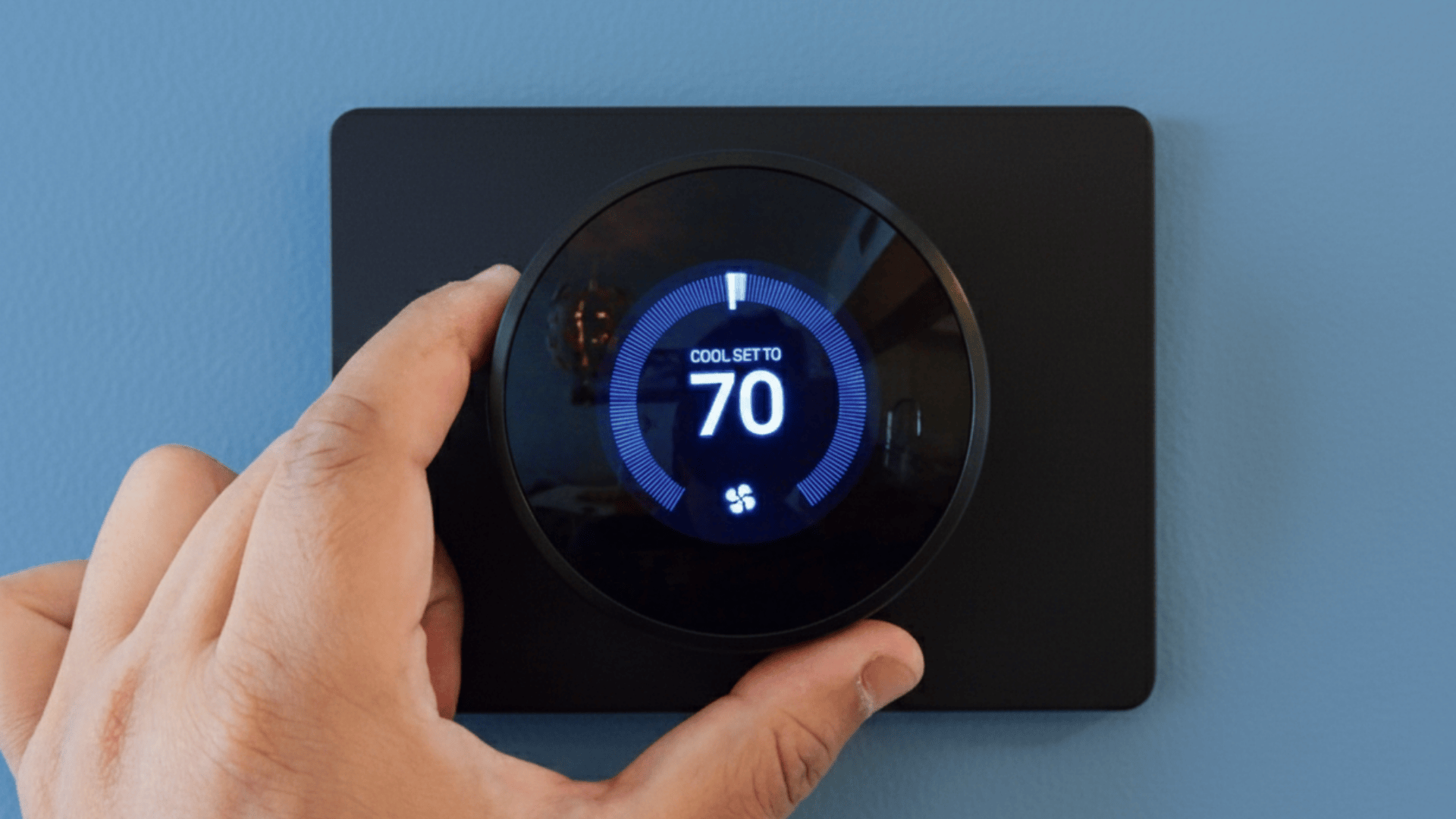
Smart thermostats serve as the control center, communicating with various sensors throughout the space.
The system connects to your smartphone or computer, enabling remote monitoring and control from anywhere.
This connectivity provides insights into energy usage, system performance, and maintenance needs that older systems cannot offer.
How Smart HVAC Systems Work?
Smart HVAC technology uses three interconnected processes to maintain ideal indoor conditions, providing automated climate control by adjusting temperature, humidity, and air quality for optimal comfort.
1. Sensors and Data Collection
Environmental sensors placed throughout the building continuously measure temperature, humidity levels, and air quality indicators.
Occupancy sensors detect when rooms are in use or empty, providing valuable information about space utilization. These devices monitor outdoor weather conditions to anticipate heating and cooling demands.
- Temperature and humidity sensors
- Occupancy and motion detectors
- Air quality monitoring devices
- Outdoor weather tracking systems
The sensors transmit data to the central control unit every few minutes, creating a comprehensive picture of the indoor environment that enables intelligent system responses.
2. System Controls and Automation
The control unit processes incoming sensor data using programmed algorithms and machine learning capabilities.
Based on this analysis, the system automatically adjusts heating, cooling, and fan speeds to maintain desired conditions. It creates different climate zones within a building, directing conditioned air only where needed.
- Automated temperature adjustments
- Zone-based climate control
- Schedule-based operation modes
- Learning user preferences over time
Smart controls consider your historical preferences and seasonal patterns. The system balances comfort requirements with energy efficiency goals, making micro-adjustments that older thermostats cannot perform while maintaining consistent indoor conditions.
3. Connectivity and Remote Access
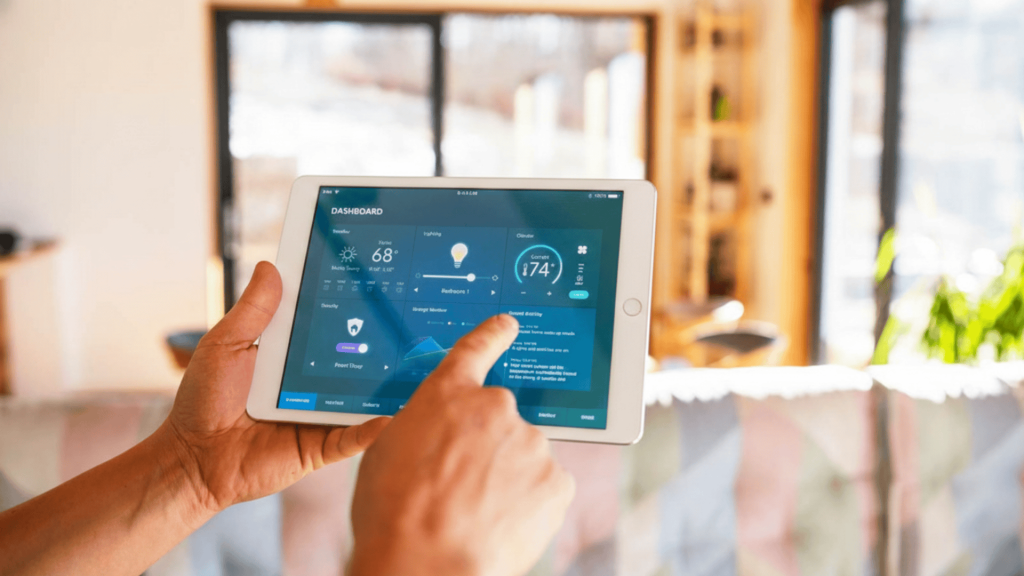
Cloud-based platforms connect your HVAC system to smartphones, tablets, and computers through dedicated apps.
These interfaces display current temperature readings, humidity levels, and system status in real-time. You can adjust settings remotely, change schedules, or switch operating modes from anywhere with internet access.
- Mobile app control and monitoring
- Real-time system status updates
- Energy consumption dashboards
- Maintenance alerts and notifications
The connectivity features enable system diagnostics and maintenance tracking. Some platforms integrate with smart home ecosystems, allowing voice control through virtual assistants while providing transparency and control that traditional HVAC systems lack.
What are the Key Components of Smart HVAC Systems?
Smart HVAC installations consist of several interconnected elements that work together as an integrated system.
Each component plays a specific role in monitoring conditions, processing information, and controlling climate operations throughout the building.
- Smart thermostats with touchscreen displays
- Environmental sensors for temperature and humidity
- Control units and software platforms
- Integration with building automation systems
Advanced models include zone dampers that direct airflow to specific areas and variable-speed fans that adjust output based on demand.
The software platform ties everything together, providing user interfaces and automated decision-making capabilities.
What are Smart Heating and Cooling Thermostats?
The smart thermostat acts as the brain of your HVAC system, coordinating all climate control functions from a single interface.
Modern smart thermostats feature Wi-Fi connectivity, touchscreen displays, and learning algorithms that adapt to your schedule and preferences.
These devices connect to your smartphone through dedicated apps, allowing remote temperature adjustments and real-time energy monitoring.
They integrate with voice assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant for hands-free control.
Advanced models use geofencing technology to detect when you leave or return home, automatically adjusting settings to maximize energy savings while maintaining comfort.
Benefits of Using Smart HVAC Systems
Modern climate control technology offers multiple advantages that impact both daily comfort and long-term operational costs.
- Improved energy efficiency: Automated adjustments reduce heating and cooling waste, typically lowering utility bills by 15-30% compared to traditional systems
- Stable indoor comfort: Precise temperature and humidity control eliminates hot and cold spots throughout the building
- Early detection of system issues: Continuous monitoring identifies performance problems before they cause complete system failures or expensive repairs
- Better control through usage insights: Detailed energy reports show consumption patterns and help optimize settings for your specific space
- Reduced environmental impact: Lower energy consumption decreases your carbon footprint and greenhouse gas emissions from heating and cooling
- Extended equipment lifespan: Optimized operation reduces mechanical stress on components, potentially adding years to your system’s useful life
Common Use Cases and Applications
Smart HVAC technology adapts to various building types and operational needs. Here are the most common applications where these systems make a significant impact.
- Residential spaces: Homeowners install smart systems to reduce energy costs, control temperatures remotely, and maintain comfort while away from home for extended periods
- Commercial buildings: Office complexes, retail stores, and hotels use smart HVAC to manage multiple zones efficiently, accommodate varying occupancy throughout the day, and reduce operational expenses
- Industrial environments: Manufacturing facilities and warehouses rely on precise climate control for product quality, worker comfort, and equipment protection in large spaces with specific temperature requirements
- Educational facilities: Schools and universities implement smart systems to condition classrooms based on class schedules, saving energy during breaks, weekends, and summer months
- Healthcare settings: Hospitals and medical offices use advanced climate control to maintain strict temperature and air quality standards required for patient care and equipment operation
Conclusion
Smart HVAC systems represent a significant advancement in climate control technology for modern buildings.
These intelligent solutions combine sensors, automation software, and connectivity features to manage heating, cooling, and ventilation more effectively than traditional equipment.
By continuously monitoring conditions and making automatic adjustments, they maintain comfortable indoor environments while reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
The technology provides valuable insights into system performance, enabling proactive maintenance and informed decision-making about energy usage.
As buildings become more connected and energy efficiency grows increasingly important, such smart systems offer practical benefits for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Do these advanced climate control capabilities align with your space requirements and comfort goals?
Share your thoughts and experiences with these smart systems in the comments below.